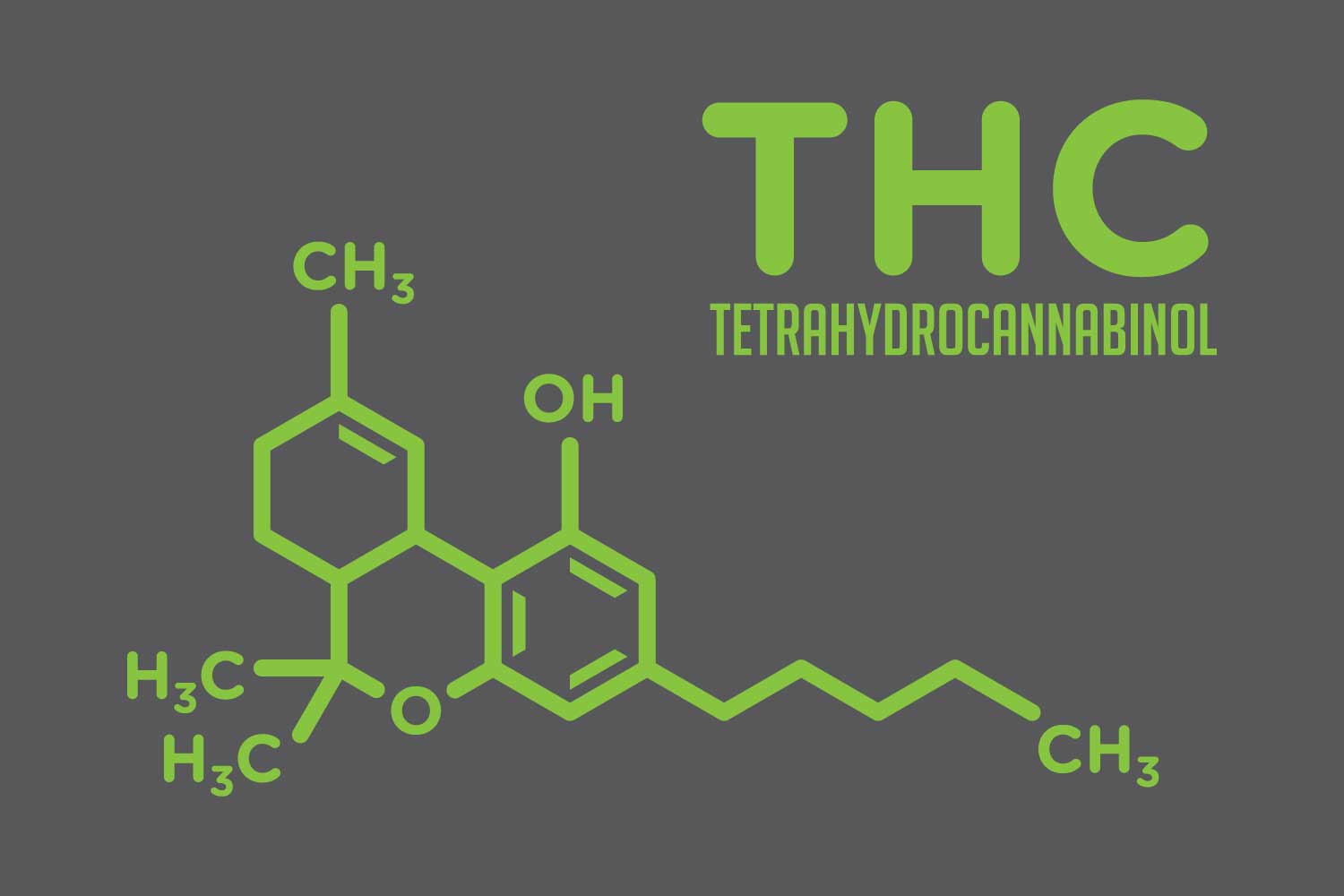
THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) is one of the most well-known chemical compounds found in the cannabis plant. It is a psychoactive compound that is responsible for the "high" feeling that people experience when they use marijuana. THC is just one of the many cannabinoids found in cannabis, but it is the most well-known and studied one.
THC interacts with the endocannabinoid system in the human body, which is responsible for regulating various physiological processes such as mood, appetite, pain, and inflammation. When THC enters the body, it binds to cannabinoid receptors in the brain and activates them, which leads to the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter that is associated with pleasure and reward.
This is what causes the euphoria and relaxation that people experience when they use marijuana. THC can also alter perception and distort the sense of time, which can lead to a feeling of time dilation.
Aside from its psychoactive effects, THC also has several medicinal properties. It is commonly used in the treatment of chronic pain, nausea and vomiting associated with chemotherapy, muscle spasms, and glaucoma. THC has also been shown to have anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties, which may be useful in the treatment of conditions such as multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer's disease.
Despite its medicinal benefits, THC is a controlled substance in many parts of the world and is illegal to possess or use without a prescription or license. The use of THC can have several side effects, such as short-term memory impairment, impaired motor coordination, and increased heart rate. Long-term use of THC can also lead to addiction and other health problems.
In conclusion, THC is a chemical compound found in the cannabis plant that is responsible for its psychoactive effects. It interacts with the endocannabinoid system in the body and can produce feelings of euphoria and relaxation. While it has several medicinal benefits, it is still a controlled substance and should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
THC interacts with the endocannabinoid system in the human body, which is responsible for regulating various physiological processes such as mood, appetite, pain, and inflammation. When THC enters the body, it binds to cannabinoid receptors in the brain and activates them, which leads to the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter that is associated with pleasure and reward.
This is what causes the euphoria and relaxation that people experience when they use marijuana. THC can also alter perception and distort the sense of time, which can lead to a feeling of time dilation.
Aside from its psychoactive effects, THC also has several medicinal properties. It is commonly used in the treatment of chronic pain, nausea and vomiting associated with chemotherapy, muscle spasms, and glaucoma. THC has also been shown to have anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties, which may be useful in the treatment of conditions such as multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer's disease.
Despite its medicinal benefits, THC is a controlled substance in many parts of the world and is illegal to possess or use without a prescription or license. The use of THC can have several side effects, such as short-term memory impairment, impaired motor coordination, and increased heart rate. Long-term use of THC can also lead to addiction and other health problems.
In conclusion, THC is a chemical compound found in the cannabis plant that is responsible for its psychoactive effects. It interacts with the endocannabinoid system in the body and can produce feelings of euphoria and relaxation. While it has several medicinal benefits, it is still a controlled substance and should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.













Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.